DBMS - (5) JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)
Javascript Object Notation(JSON) 특성
- Standrad for 'serializing' data objects, usually in files
- Human-readable, useful for data interchange
- Also useful for representing & storing semi-structured data
- No longer tied to JavaScript
- Parsers for many languages.
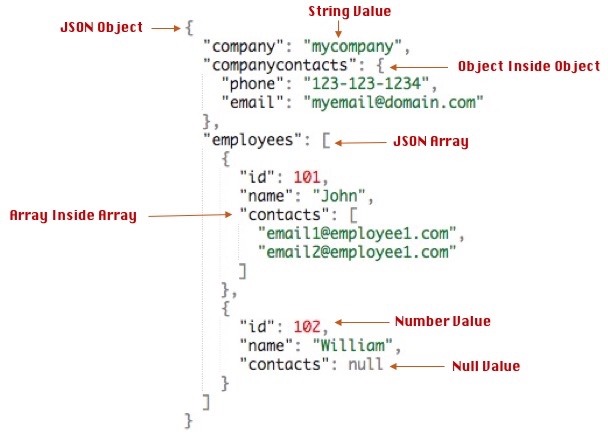
Basic constructs(recursive)
- Base values : numbers, string, boolean, etc...
- Object {} : sets of label-value(=property) pairs
- Arrays [] : list of values
Relational Model versus JSON
| Relational Model | JSON | |
| Structure | Tables | Sets of nested arrays |
| Schema | Fixed in advance | 'self-describing' : schema elements are within the data itself |
| Queries | Simple Expressive language | nothing |
| Ordering | none | Arrays |
| Implementation | Native systems | Coupled with programming language NoSQL system |
XML versus JSON
| XML | JSON | |
| Verbosity(쓸데없는 meta-data) | More | Less |
| Complexity | More | Less |
| Validity | Document Type Descriptor(DTD), XSD | JSON Schema(not widely used) |
| Programming Interface | clunky(impedance mismatch) | More direct |
| Querying | XPath, XQuery | nothing |
Reference
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JwSWIC6fJ5Q&list=PL6hGtHedy2Z4EkgY76QOcueU8lAC4o6c3&index=7
'데이터베이스' 카테고리의 다른 글
| DBMS - (7) Relational Algebra - set operator, renaming (0) | 2019.06.27 |
|---|---|
| DBMS - (6) Relational Algebra - select, project, join (0) | 2019.06.27 |
| DBMS - (4) XML(Extensible Markup Language) (0) | 2019.06.27 |
| DBMS - (3) Querying Relational Databases (0) | 2019.06.27 |
| DBMS - (2) The Relational Model (0) | 2019.06.27 |


